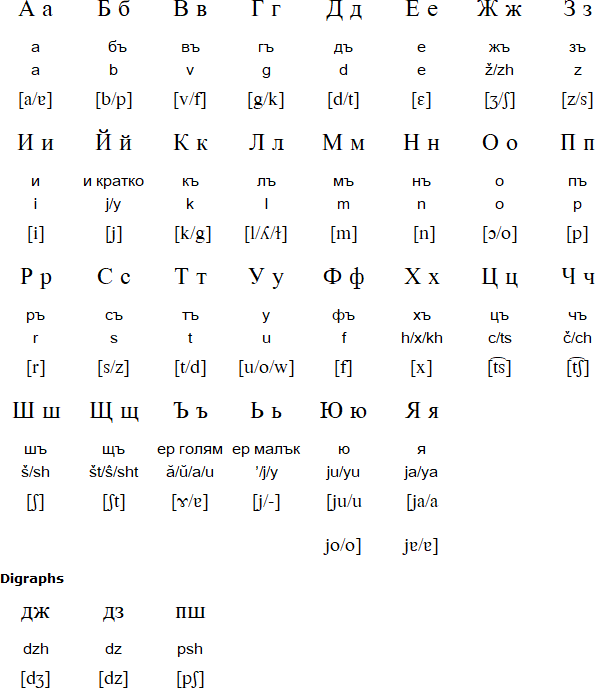Difference between revisions of "Bulgaria Travel Fact Sheet"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{#eimage:http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/94/Oilcape.jpg|410x579px|thumb|'''[[Bulgaria]].'''<BR/>Source: wikipedia.org.}} | ||
| + | |||
=Basic Info= | =Basic Info= | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
==Ethnic Groups== | ==Ethnic Groups== | ||
| − | + | Bulgarians are the main ethnic group and comprise 84.8 per cent of the population. Turkish and Roma minorities comprise 8.8 and 4.9 per cent, respectively; some 40 smaller minorities comprise 0.7 per cent, and 0.8 per cent do not self-identify with an ethnic group.[242] All ethnic groups speak Bulgarian, either as a first or as a second language | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==U.S. Embassy== | ==U.S. Embassy== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 49: | ||
==Major Languages Spoken== | ==Major Languages Spoken== | ||
| − | Bulgarian | + | Bulgarian (български език, pronounced [ˈbɤ̞ɫɡɐrski ɛˈzik]) is an Indo-European language, a member of the Southern branch of the Slavic language family. |
| + | |||
| + | Bulgarian, along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), has several characteristics that set it apart from all other Slavic languages: changes include the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article (see Balkan language area), and the lack of a verb infinitive, but it retains and has further developed the Proto-Slavic verb [[system]]. Various evidential verb forms exist to express unwitnessed, retold, and doubtful action. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Based on the 2011 census, Ethnologue estimates that Bulgarian is spoken as a native language by 6.8 million | ||
==Alphabet== | ==Alphabet== | ||
| − | Cyrillic | + | {{#eimage:http://www.omniglot.com/images/writing/bulgarian.gif|410x579px|thumb|'''Bulgarian Alphabet.'''<BR/>Source: omniglot.com.}} |
| + | |||
| + | Bulgarian is a Southern Slavic language with about 12 million speakers mainly in [[Bulgaria]], but also in [[Ukraine]], [[Macedonia]], [[Serbia]], [[Turkey]], [[Greece]], [[Romania]], [[Canada]], USA, [[Australia]], [[Germany]] and [[Spain]]. Bulgarian is mutually intelligible with Macedonian, and fairly closely related to Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Slovenian. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bulgarian was the first Slavic language to be written: it start to appear in writing during the 9th century in the Glagolitic alphabet, which was gradually replaced by an early version of the Cyrillic alphabet over the following centuries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | At the end of the 18th century the Russian version of Cyrillic or the "civil script" of Peter the Great (1672-1725) was adapated to write Bulgarian as a result of the influence of printed books from [[Russia]]. During the 19th century a number of versions of this alphabet containing between 28 and 44 letters were used. In the 1870s a version of the alphabet with 32 letters proposed by Marin Drinov became widely used. This version remained in use until the orthographic reform of 1945 when the letters yat (Ѣ ѣ), and yus (Ѫ ѫ) were removed from the alphabet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A modern literary language based on vernacular spoken Bulgarian was standardised after [[Bulgaria]] became independent in 1878. Many Turkish words were [[adopted]] into Bulgarian during the long period of Ottoman rule. Words have also been borrowed from Latin, Greek, Russian, French, Italian, German and increasingly from English. | ||
==Major holidays== | ==Major holidays== | ||
| Line 76: | Line 87: | ||
Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bulgaria Wikipedia] | Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bulgaria Wikipedia] | ||
Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_holidays_in_Bulgaria Bulgarian Holidays] | Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_holidays_in_Bulgaria Bulgarian Holidays] | ||
| + | Source: [http://www.omniglot.com/writing/bulgarian.htm Bulgarian Alphabet] | ||
| + | Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bulgarian_language Wikipedia Bulgarian Language] | ||
[[Category: Bulgaria Adoption]] | [[Category: Bulgaria Adoption]] | ||
[[Category: Traveling to Bulgaria]] | [[Category: Traveling to Bulgaria]] | ||
Revision as of 20:09, 18 June 2014
Contents
Basic Info
Country Name
Official Name: The Republic of Bulgaria
What the People are Called
Bulgarians
Ethnic Groups
Bulgarians are the main ethnic group and comprise 84.8 per cent of the population. Turkish and Roma minorities comprise 8.8 and 4.9 per cent, respectively; some 40 smaller minorities comprise 0.7 per cent, and 0.8 per cent do not self-identify with an ethnic group.[242] All ethnic groups speak Bulgarian, either as a first or as a second language
U.S. Embassy
16 Kozyak Street Sofia 1408 Bulgaria Tel: (359 2) 937-5100 Fax: (359 (2) 937-5122 Email: iv_sofia@state.gov Internet: http://bulgaria.usembassy.gov
Canadian Embassy
7, Pozitano street, block no. 3, first floor, office no. 4 Postal code 1301 1000 Sofia, Bulgaria Tel: + 359-2-969-9710 Fax: + 359-2-981-6081 E-mail: general@canada-bg.org
Currency
Bulgarian Lev
Time Zone
Summer (DST)
Phone/Internet Information
Calling code +359 Internet TLD .bg
Major Languages Spoken
Bulgarian (български език, pronounced [ˈbɤ̞ɫɡɐrski ɛˈzik]) is an Indo-European language, a member of the Southern branch of the Slavic language family.
Bulgarian, along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), has several characteristics that set it apart from all other Slavic languages: changes include the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article (see Balkan language area), and the lack of a verb infinitive, but it retains and has further developed the Proto-Slavic verb system. Various evidential verb forms exist to express unwitnessed, retold, and doubtful action.
Based on the 2011 census, Ethnologue estimates that Bulgarian is spoken as a native language by 6.8 million
Alphabet
Bulgarian is a Southern Slavic language with about 12 million speakers mainly in Bulgaria, but also in Ukraine, Macedonia, Serbia, Turkey, Greece, Romania, Canada, USA, Australia, Germany and Spain. Bulgarian is mutually intelligible with Macedonian, and fairly closely related to Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Slovenian.
Bulgarian was the first Slavic language to be written: it start to appear in writing during the 9th century in the Glagolitic alphabet, which was gradually replaced by an early version of the Cyrillic alphabet over the following centuries.
At the end of the 18th century the Russian version of Cyrillic or the "civil script" of Peter the Great (1672-1725) was adapated to write Bulgarian as a result of the influence of printed books from Russia. During the 19th century a number of versions of this alphabet containing between 28 and 44 letters were used. In the 1870s a version of the alphabet with 32 letters proposed by Marin Drinov became widely used. This version remained in use until the orthographic reform of 1945 when the letters yat (Ѣ ѣ), and yus (Ѫ ѫ) were removed from the alphabet.
A modern literary language based on vernacular spoken Bulgarian was standardised after Bulgaria became independent in 1878. Many Turkish words were adopted into Bulgarian during the long period of Ottoman rule. Words have also been borrowed from Latin, Greek, Russian, French, Italian, German and increasingly from English.
Major holidays
January 1 New Year's Day January 2 Day after New Year's Day March 3 Liberation Day Moveable Good Friday Moveable Easter Moveable Easter Monday May 1 Labour Day May 6 St. George's Day May 24 Bulgarian Education and Culture, and Slavonic Literature Day September 6 Unification Day September 22 Independence Day November 1 Revival Leaders' Day December 24 Christmas Eve December 25 Christmas Day December 26 Second Day of Christmas
Source: Wikipedia Source: Bulgarian Holidays Source: Bulgarian Alphabet Source: Wikipedia Bulgarian Language